Imagine being able to take out a loan, swap currencies, or earn interest on your savings — without a bank, without paperwork, and without waiting for approval from a manager. That’s exactly what DeFi offers. Decentralized finance provides always-on, permissionless access to financial services for anyone with an internet connection. In this guide, we’ll explain what DeFi is, how it works, and why it has the potential to change the way you manage money.
DeFi (short for «Decentralized Finance») refers to blockchain-based financial services that operate without intermediaries. Instead of banks, brokers, or centralized exchanges, DeFi relies on automated programs called smart contracts. These contracts handle everything on their own — transfers, interest payments, loans, and more.
Smart contracts are written by developers and engineering teams. Their code defines the platform’s rules: how interest rates are set, how rewards are distributed, and how funds move. But how can you know whether that code is trustworthy? We’ll get to that in a moment.
How DeFi Works: The Core Principles
To understand DeFi, you need to know three key components: smart contracts, blockchains, and crypto wallets. Don’t worry — we’ll keep things beginner-friendly.
Smart Contracts: Automated «Executors» of Transactions
A smart contract is a blockchain program that automatically enforces the terms of an agreement. Think of it like a vending machine: you insert money, choose a drink, and the machine delivers it instantly. The payment check and the delivery happen automatically — no cashier needed.
DeFi smart contracts work the same way. For example, when you deposit crypto to earn interest:
- You send your tokens to a smart contract.
- The contract automatically accrues interest with every block (about every 12 seconds on Ethereum).
- You can withdraw your funds with the accumulated interest at any time.
No bank clerks, no paperwork, no account maintenance fees.
💡 Tip: Smart contracts follow the code exactly. If the conditions are met, the transaction happens. If they’re not, it doesn’t. No one can change the rules on the fly.
How Can You Trust Smart Contracts?
A reasonable concern is: what if the developer wrote buggy code, or worse, included a hidden backdoor? Why trust a program written by strangers?
DeFi uses several layers of protection:
Open-Source Code
Smart contract code is public. Anyone can inspect it and look for mistakes or vulnerabilities. It’s like being able to walk into a restaurant’s kitchen and see exactly how your food is made. Traditional banks don’t give you that kind of transparency.
Independent Security Audits
Serious projects hire specialized firms — such as ConsenSys Diligence, Trail of Bits, and OpenZeppelin — to review their code. Think of it as a professional engineering inspection for a house. For example, Aave has undergone more than 15 independent audits.
Bug Bounty Programs
Many platforms pay rewards to anyone who finds vulnerabilities. Critical discoveries can earn up to $250,000. This encourages hackers to report issues ethically instead of exploiting them.
Reputation and Track Record
The longer a project runs without major incidents, the more trust it earns. Platforms like MakerDAO and Uniswap have been operating for years, surviving market crashes, and proving their reliability.
Decentralized Governance (DAO)
Many projects eventually hand control to their communities through a DAO — «Decentralized Autonomous Organization». Any changes to the protocol require a token-holder vote. Harmful proposals get rejected by the community.
Timelocks for Major Changes
Even after a vote, updates don’t go live instantly. Most protocols have a 24–48 hour timelock, giving users time to withdraw funds if they disagree with a change.
❗️Important: Even with these protections, DeFi still carries risks. New projects without audits or a track record are especially dangerous. In DeFi, the rule of thumb is simple: the more established and battle-tested a platform is, the safer it tends to be.
Blockchain: A Transparent Public Ledger
A blockchain is a public ledger that records every transaction. Anyone can see how much money is locked in a specific smart contract, what transactions are happening, and how much each address has earned. If you want a deeper breakdown of how the technology works, check out our guide «What Is Cryptocurrency? Simple Guide for Beginners», where we explain blockchain mechanics in detail.
In a traditional bank, you only see your own account, while the bank sees everyone’s — and it doesn’t have to share that information with you. In DeFi, it’s the opposite: everything is open. The only difference is that you won’t see real names — just wallet addresses (long strings like «0x742d35Cc6634C0532925a3b844Bc9e7595f0bEb»).
❗️Important: Blockchain transparency is both a strength and a drawback. On one hand, no one can manipulate the data or hide suspicious activities. On the other hand, all your transactions are visible to the public (though not tied to your real identity).
Crypto Wallets: Your Personal Bank
DeFi doesn’t use traditional bank accounts. Instead, you interact with your assets through a crypto wallet — an app that serves as your interface to the blockchain. The most widely used wallets in DeFi are MetaMask and Trust Wallet. If you haven’t created a wallet yet, we have a step-by-step guide «How to Create a Crypto Wallet in 5 Minutes» that walks you through the entire process.
The key difference from a bank account: you control your funds entirely. A bank can’t freeze your wallet, a government can’t seize your assets, and you can send crypto to anyone, anywhere — even at 3 a.m. on a Sunday.
⚡️ Crucial to know: Your secret recovery phrase (12–24 words) is the only key to your crypto wallet. Lose it — and you permanently lose access to your funds. To learn how to store your seed phrase safely, read our guide «Seed Phrase: What It Is, Why It Matters, and How to Protect Your Crypto».
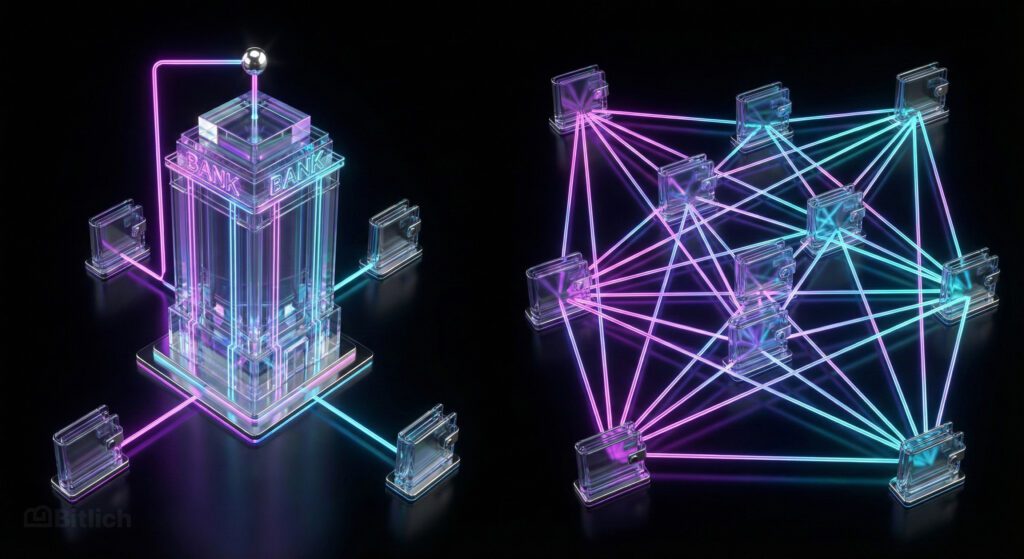
How DeFi Differs From Traditional Banking
Traditional finance is often referred to as CeFi («Centralized Finance») because all operations pass through central institutions: banks, exchanges, and payment processors. DeFi works differently — with no central authority. Here’s a clear comparison between decentralized finance and the traditional banking system:
| Parameter | Traditional Finance (Banks) | DeFi |
|---|---|---|
| Access | Requires documents, proof of address, sometimes credit history | Internet access and a crypto wallet are enough |
| Operating hours | Business hours (typically 9:00–18:00 on weekdays) | 24/7, including weekends and holidays |
| Intermediaries | Banks, exchanges, payment processors charge fees | Only pay the blockchain transaction fee |
| Control over funds | A bank can freeze or restrict your account | Only you control your money |
| Transaction speed | Transfers take 1–3 days; international can take a week | Minutes (depends on the network) |
| Transparency | You see only your own account | All transactions are public and verifiable |
| Geographic limitations | Depends on country and regulations | Works globally with no borders |
👉 Example: A traditional international bank transfer may take 3–5 days and cost $20–50 in fees. In crypto (including DeFi), transfers usually take just a few minutes with fees ranging from a few cents to around $10 — depending on the network.
What Services DeFi Offers
DeFi isn’t a single platform — it’s a full ecosystem of financial services. In essence, it’s a decentralized alternative to the entire banking system. Here’s what you can do in DeFi:
Basic Financial Operations:
- Swap one cryptocurrency for another without intermediaries (decentralized exchanges).
- Store assets in stablecoins to reduce exposure to volatility.
Earning and Investing:
- Earn interest by depositing crypto (similar to a savings account).
- Lend assets to other users and earn interest.
- Staking — earn rewards by helping secure a blockchain network.
- Provide liquidity to pools and earn a share of trading fees.
- Yield farming — combine strategies to maximize returns.
Borrowing:
- Take out loans backed by crypto collateral with no credit checks.
- Flash loans — instant, uncollateralized loans (for advanced users).
Advanced Tools:
- Trade derivatives and futures.
- Create synthetic assets (e.g., tokenized stocks and commodities).
- Use decentralized insurance protocols to protect against risks.
- Participate in protocol governance through a DAO («Decentralized Autonomous Organization»).
Up next, we’ll explore these categories in detail.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEX)
A decentralized exchange (DEX) lets you swap one cryptocurrency for another directly, without intermediaries. You simply connect your wallet, choose the assets you want to trade, and the transaction is executed automatically through a smart contract.
How It Works: Instead of relying on a traditional order book where buyers and sellers place orders, DEXs use liquidity pools. These pools work like «reservoirs» of tokens contributed by users. Traders exchange assets against these pools and pay a small fee (typically around 0.3%), which is distributed among liquidity providers.
Popular DEX Platforms:
- Uniswap — the largest decentralized exchange with roughly $2.3B in daily trading volume. It operates across multiple networks, including Ethereum, Arbitrum, Polygon, Base, and BNB Chain.
- PancakeSwap — a major DEX on BNB Chain, known for low transaction fees.
💡 Tip: DEXs don’t require registration or KYC. Just connect your wallet and start trading.
Lending and Borrowing
In DeFi, you can lend your crypto to earn interest or borrow funds by using your assets as collateral.
How to Earn by Lending: You deposit your tokens (for example, USDT or ETH) into a lending protocol. Other users borrow these funds and pay interest, and you receive a share of those payments. Rates typically range from 3% to 15% annually, depending on demand.
How Borrowing Works: To borrow in DeFi, you lock up collateral. For example, you might deposit $1,000 worth of ETH and borrow $600–700 in stablecoins (collateral ratios usually fall between 130–150%). If the value of your collateral drops below the required threshold, the smart contract automatically sells it to repay the loan — this process is called liquidation.
Popular Lending Platforms:
- Aave — the largest lending platform with over $20B in total value locked (TVL). It offers stable and variable rates, flash loans, and supports multiple blockchains.
- Compound — one of the earliest lending protocols, adjusting interest rates algorithmically based on supply and demand.
If you want detailed walkthroughs for using platforms like Aave or Lido to earn passive income, check out our guide «How to Earn Passive Crypto Income».
❗️Important: DeFi loans don’t require credit checks. Everything is collateral-based — if you fail to repay, you lose your collateral.
Staking and Liquidity Pools
Staking and liquidity provision are popular ways to earn passive income with cryptocurrency.
Staking: You lock your tokens to help secure a blockchain network and receive rewards. For example, staking ETH through Lido yields around 3–4% annually. You also receive stETH, a token you can use in other DeFi protocols while still earning staking rewards.
Liquidity Pools: You deposit a pair of tokens (for example, ETH and USDT) into a liquidity pool on a decentralized exchange. In return, you earn a share of the trading fees generated by swaps inside that pool. Returns can reach 8–20% annually, but be aware of the risk of «impermanent loss» — when token prices diverge from each other significantly.
Popular Staking Platforms:
- Lido — the largest liquid staking protocol with more than $30B locked. It allows you to earn staking rewards while keeping your assets liquid.
- Rocket Pool — a decentralized alternative to Lido that lets users run validator nodes with just 16 ETH instead of the usual 32.
💰 Stats: Liquidity providers on decentralized exchanges have earned more than $815M in fees, with over 90% generated on Uniswap.
Stablecoins in DeFi
Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies pegged to stable assets (usually the US dollar). They help reduce exposure to market volatility while keeping all the advantages of DeFi.
It’s important to understand that there are two main types of stablecoins:
Centralized Stablecoins (CeFi Elements Inside DeFi):
- USDT (issued by Tether) and USDC (issued by Circle) are backed by real dollars held in company bank accounts.
- While they are widely used across the DeFi ecosystem, they remain part of centralized finance (CeFi).
- Issuers must maintain reserves and undergo audits to prove their backing.
- Risk: The issuing company can freeze your tokens or mismanage reserves.
Decentralized Stablecoins (Pure DeFi):
- DAI (created by MakerDAO) is generated by locking collateral in smart contracts. Its stability around $1 is maintained through overcollateralization and automated on-chain mechanisms.
- No company controls DAI — governance is handled through decentralized voting.
- This makes it more resistant to censorship or asset freezes, though technically more complex.
Stablecoins let you hold «dollars» inside DeFi, earn interest, use them for lending or trading, and avoid 10–20% daily price swings typical for volatile crypto assets.
Advantages of DeFi
Why are more people turning to decentralized finance? Here are the key benefits:
Accessibility for Everyone
You don’t need documents, a bank account, or a credit history to use DeFi. A smartphone with internet access is enough. According to the World Bank, around 1.7 billion adults worldwide are unbanked — DeFi gives them a way to access the global financial system.
Always On
DeFi protocols operate 24/7, 365 days a year. You can borrow, swap currencies, or withdraw funds anytime — even at 3 a.m. on New Year’s Day.
Low Fees
No intermediaries means no intermediary fees. You only pay blockchain transaction costs, typically from $1 to $20 depending on the network and congestion. For comparison: an international bank transfer can cost $20–50 plus a poor exchange rate.
Full Transparency
All smart contracts are open for inspection. You can review the protocol’s code, see every transaction, and check how much value is locked. This eliminates hidden fees and opaque practices sometimes found in traditional finance.
Control Over Your Money
No one can freeze your account, restrict withdrawals, or block your transactions. You decide what happens to your assets. This is especially valuable for people living in countries with unstable economies or restrictive governments.
No Bureaucracy
No applications, no approvals, no waiting. Connect your wallet, click a few buttons — and the transaction is done. A DeFi loan takes two minutes instead of two weeks at a bank.
💡 Tip: Despite the advantages, DeFi isn’t ideal for everyone. If you feel more comfortable with traditional banking and prefer not to take full responsibility for securing your own assets, start by learning — not by investing right away.
DeFi Risks: What You Need to Know
DeFi unlocks a huge range of opportunities — but with them come real risks. As Vitalik Buterin, the creator of Ethereum, notes: the DeFi sector has moved beyond its early speculative phase, but it still faces significant technical challenges and security threats. Let’s break down the main risks.
Technical Risks
Smart Contract Bugs
Smart contracts are written by people — and people make mistakes. A single error in the code can lead to millions of dollars lost. For example, in August 2021 the Poly Network protocol was hacked, resulting in a $611 million theft — the largest exploit in DeFi history.
How to protect yourself: choose platforms that have undergone code audits by reputable firms such as ConsenSys Diligence, Trail of Bits, or OpenZeppelin. The more audits, the better. For instance, Aave has gone through more than 15 independent security reviews.
Hacks and Vulnerabilities
Hackers constantly probe DeFi platforms for weaknesses. The more complex the protocol and the more features it has, the higher the chance that something can be exploited — especially with newer projects that haven’t been tested over time.
❗️Important: Research shows that DeFi security has improved significantly in recent years, but risks still remain.
Financial Risks
Crypto Volatility
Cryptocurrency prices can swing dramatically. If you take a loan using ETH as collateral and its price drops 30%, your collateral may be automatically liquidated to repay the debt. In that case, you lose the collateral and pay a liquidation penalty (typically 5–15%).
Impermanent Loss
If you provide liquidity to a pool — for example, ETH/USDT — and the price of ETH changes significantly, you may end up with less profit than if you had simply held your tokens. In the worst case, even the earned fees won’t fully offset the loss.
Stablecoin Risk
Even stablecoins can lose their peg during crises. In May 2022, the UST stablecoin collapsed entirely, dragging down the entire Terra ecosystem and wiping out tens of billions of dollars.
User Risks
Losing Access to Your Wallet
If you lose your seed phrase, no one can restore access to your funds. They become permanently inaccessible. Unlike traditional finance, there is no support team that can reset your password — this applies to both DeFi and regular crypto storage.
Phishing and Scams
Scammers create fake DeFi websites, send phishing links, and impersonate support teams. One wrong click can give attackers access to your wallet. Always verify the website’s address, never share your seed phrase, and rely only on official sources.
Regulatory Risks
Governments around the world are working on DeFi regulation. Some protocols may face restrictions or even bans in certain countries. For example, Turkey blocked access to the decentralized exchange PancakeSwap.
⚠️ Remember: A rising TVL («total value locked») doesn’t always mean a protocol is reliable. Sometimes it’s just marketing or short-term hype. Always check how long the protocol has been operating and what reputation it has within the community.
The Future of DeFi
The decentralized finance ecosystem continues to evolve at a rapid pace. Here are the key trends shaping the future of DeFi:
Integration With Traditional Finance
DeFi and traditional financial institutions (TradFi) are gradually converging. Banks are beginning to offer DeFi-based services to their clients, while DeFi protocols are increasingly working with real-world assets such as stocks, bonds, and real estate. Analysts predict that the market for tokenized real-world assets could reach $30 trillion within the next decade.
Mainstream Adoption of Stablecoins
Stablecoins are set to become widely used for international transfers and everyday payments. Major payment networks are already integrating them into their services, bringing crypto into the daily lives of millions.
Improved Security
New audit standards, automated vulnerability detection tools, and bug bounty programs offering up to $250,000 for critical findings are emerging. Platforms are adopting multilayered security mechanisms, dedicated safety modules, and decentralized insurance.
Simplified User Interfaces
DeFi platforms are becoming increasingly beginner-friendly. New solutions hide the technical complexity, making DeFi feel as easy as using a regular banking app.
Cross-Chain Interoperability
Barriers between blockchains are disappearing. Protocols now support multiple networks, allowing users to move assets seamlessly and access the best opportunities regardless of which blockchain they’re on.
Automated Strategies
Advanced tools are emerging that automatically allocate assets for maximum returns. Yield aggregators monitor dozens of protocols and move funds to the best-performing options automatically.
👉 Analysts project that the DeFi market could grow at an annual rate of around 20%, reaching more than $231 billion in the coming years.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How much money do I need to start using DeFi?
Technically, you can start with any amount. However, due to transaction fees (gas fees), it’s recommended to begin with at least $100–200. On blockchains like BNB Chain or Polygon, fees are much lower than on Ethereum, so you can start with smaller amounts.
Do I have to pay taxes on DeFi income?
Yes. In most countries, earnings from crypto activity are taxable — including profits from token swaps, staking rewards, and lending interest. Tax rules vary by jurisdiction, so it’s best to consult a tax professional.
Can I lose money in DeFi even if I’m not trading?
Yes, there are several risks:
- Impermanent loss when providing liquidity.
- Market volatility — your crypto can drop in value.
- Platform hacks or smart contract vulnerabilities.
- Stablecoins losing their peg.
How is DeFi different from a crypto exchange like Binance?
Binance is a centralized exchange (CEX). The company controls your funds and can freeze your account. In DeFi, you control your money through your own wallet. CEX platforms require registration and identity verification, while DeFi does not. CEX platforms are often easier for beginners, but DeFi offers more freedom and flexibility for experienced users.
Can you recover funds if you send them to the wrong address?
No. Blockchain transactions are irreversible. Theoretically, you could recover funds if you know the owner of the address and they agree to return them — but in practice, the money is almost always lost. Always double-check the address before sending.
Are funds in DeFi insured?
Unlike bank deposits, DeFi funds are not government-insured. However, decentralized insurance protocols such as Nexus Mutual allow you to insure against smart contract hacks — but this is an additional paid service.
Which blockchain is best for DeFi?
It depends on your priorities:
- Ethereum — the largest DeFi ecosystem, but high transaction fees ($5–50).
- Binance Smart Chain — low fees ($0.20–1), many popular projects, but more centralized.
- Polygon — low fees and strong compatibility with Ethereum.
- Solana — very fast and extremely low-cost transactions, with a growing DeFi ecosystem.
For beginners, Polygon or BNB Chain is often recommended due to low fees.
Do I need technical skills to use DeFi?
Only basic skills: installing a wallet, understanding wallet addresses, and sending transactions. No programming required. But you should understand the risks and research each platform before using it. Start with small amounts and simple actions, expanding your knowledge gradually.
What is a rug pull, and how do I avoid it?
A rug pull is a scam where project creators withdraw all liquidity and disappear. Red flags include:
- Anonymous team with no reputation.
- No smart contract audit.
- Unrealistically high promised returns.
- Low liquidity in pools.
- Brand-new project with no track record.
Use only reputable platforms with audits and active communities.
Can you earn in DeFi without risk?
No. There is no such thing as a completely risk-free DeFi strategy. Even earning interest on stablecoins carries risks: depegging, protocol hacks, and smart contract bugs. A simple rule: the higher the promised return, the higher the risk.
Summary
DeFi is a financial revolution that gives people worldwide access to services without intermediaries, restrictions, or bureaucracy. Decentralized exchanges, lending protocols, staking, and other tools already provide a real alternative to traditional banking.
But remember: with great freedom comes great responsibility. There’s no deposit insurance, no customer support, and no way to reverse a mistaken transaction. You are fully responsible for the security of your assets and the decisions you make.
DeFi may be right for you if:
- You’re willing to learn and explore new technologies.
- You value full control over your money more than traditional banking convenience.
- You understand the risks and are ready to start with small amounts.
- You live in a region with limited access to financial services or want more financial freedom.
Start by learning, use only reputable platforms, never invest more than you can afford to lose, and always store your wallet’s seed phrase in a secure place. DeFi offers incredible opportunities — but only to those who approach it with awareness and responsibility.








Hello there I am so glad I found your web site, I really found you by mistake, while I was searching on Yahoo for something else, Anyways I am here now and would just like to say thanks for a marvelous post and a all round interesting blog (I also love the theme/design), I don’t have time to go through it all at the minute but I have book-marked it and also added in your RSS feeds, so when I have time I will be back to read a great deal more, Please do keep up the excellent job.